It’s a transformative moment for the Canadian nuclear industry. The country has become the first in the world to approve the construction of a grid-scale Small Modular Reactor (SMR), set to be built at Ontario Power Generation’s Darlington Nuclear site.
At the same time, Canada is making impressive strides in fusion technology, marked by a breakthrough earlier this year and the adoption of AI and digital technologies to revolutionize how services are delivered in the industry. Nuclear energy will be a key part of a suite of new energy infrastructure built to meet surging data-center power demand driven by artificial intelligence.
Several big tech companies looking for low carbon, round-the-clock energy signed contracts for new nuclear capacity in the last year, and there could be more such deals ahead. These efforts come as electricity usage by data centers is expected to more than double by 2030, according to reports led by Brian Singer, Jim Schneider, and Carly Davenport. In total, the team forecasts 85-90 gigawatts (GW) of new nuclear capacity would be needed to meet all the data center power demand growth expected by 2030 (relative to 2023).
Greg Ferguson, General Manager of Nuclear at Eclipse Automation, shares his perspective on how innovation is transforming the energy sector and its implications for the nuclear industry. In this Q&A, Greg offers valuable insights into the future of the field.

Tracey: Greg, a pleasure to be here with you! Can you tell our audience who Greg Ferguson is, please?
Greg: I’m Greg Ferguson, General Manager – Nuclear at Eclipse Automation. I lead a team of talented individuals across several disciplines including engineering, project management, and crafts or trades. We all work together to service the nuclear industry, in Canada and abroad. My journey started 18 years ago as a tool and die apprentice; I then went on to numerous positions in the nuclear industry. My experience includes leading teams on the CANDU refurbishment programs at Darlington and Bruce Power, as well as several innovation programs. I’m now in a position at Eclipse to drive change by delivering real innovation to several projects.
Tracey: Who is Eclipse Automation and how do they fit in with the nuclear ecosystem puzzle?
Greg: Eclipse Automation, is a full-service partner to the nuclear industry, offering a comprehensive suite of capabilities that span the entire project lifecycle–from concept and design, through manufacturing, delivery and service. More specifically, we provide consulting, contract manufacturing, custom automation, build-to-print, and design-and-build services, while supporting and strengthening the nuclear supply chain. What sets us apart is the ability to combine traditional engineering and proven solutions with the latest digital tools and AI–an exciting evolution for the industry.
The team brings deep experience across major projects, including the Darlington and Bruce refurbishment projects, and the upcoming Cernavoda and Qinshan projects. One of our most notable accomplishments is the first-of-its-kind custom waste management solution designed for the nuclear industry, navigating the complex regulations and operational demands to create a solution that not only achieves project goals for sorting waste, but also sets a new standard in worker safety, environmental protections. There is now potential for Eclipse, and others in the industry, to utilize these and other innovations to improve existing solutions in the nuclear industry.
It is with projects like these that we are helping to shape the future of the nuclear sector, but with the flexibility of our team we can support nuclear projects of any size and scope.
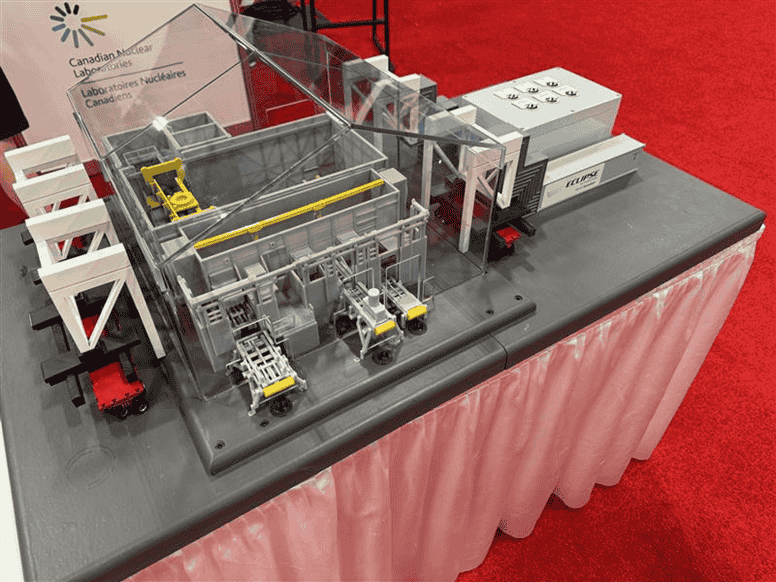
Model of the waste management system created for Whiteshell Laboratories
Tracey: Greg, how do you see the future of the nuclear industry evolving?
Greg: The nuclear industry is entering a new era of innovation, with advancements in Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), fusion, and beyond. These advancements come at a time when more countries and companies are looking for net-zero and more sustainable energy options. As a result, it is a very exciting to be in the industry, especially in Canada, which is cementing its place as a global leader in the industry.
One of the most recent and significant developments is the approval of the world’s first SMR, to be built at the Ontario Power Generation Darlington nuclear site. This milestone marks a turning point in the global energy sector and ushers in the era of greater flexibility for the industry. SMR’s are advantageous because they offer greater flexibility in terms of power generation, lower costs and easier integration with existing energy infrastructure.
Canada is also making waves with fusion technology. Earlier this year, Canadian researchers achieved a nuclear energy breakthrough by generating 600 million neutrons per second using Magnetized Target Fusion (MTF) technology. This brings the world closer to realizing the potential of commercially viable fusion energy, an ultra-clean and safe source of energy with virtually unlimited potential.
Micro-reactors is also another area with the potential to reshape remote communities, in Canada and around the world. These compact reactors have the potential to provide reliable and sustainable energy, allowing some communities to achieve energy independence for the first time.
While all these technologies, along with safety protocols, are advancing faster than ever, public opinion has not progressed along with it. Many people still have decades-old doubts about nuclear technology, despite its evolution over time. We need to foster greater public discussion and ensure that public sentiment realigns itself with the current state of the nuclear industry, working to dispel myths, old beliefs and earn the trust of the public. To do this, we need generous, honest, transparent communication and outreach, including education.
Tracey: I have been hearing nuclear has another role to play besides providing clean power in the healthcare market. Can you share more?
Greg: The world’s very first cancer treatment using isotopes to treat brain cancer happened here in Canada at Victoria Hospital in London in 1951. Since then, Canada has been at the forefront of medical discoveries using isotopes. Today, medical isotopes are expanding their impact in healthcare, with greater adoption and applications ranging from sterilization of equipment and implantable devices to providing treatment for a range of conditions, including cancer and tumors.
Canada is at the forefront of this industry, producing more than half of the worlds global supply. It has become so important that reactors at Bruce and Darlington have been outfitted to produce isotopes, and this is complemented by McMaster and other research reactors across the country. As the market for isotopes continues to grow, it is expected to reach $33 billion USD by 2031. This leaves a huge amount of opportunity for Canada to expand its reach in the global medical field and maintain its leading position in the isotope industry.
Tracey: With such an impact on the healthcare industry do you see other applications of this technology being applied elsewhere?
Greg: Technology is advancing rapidly, and while the nuclear industry has traditionally been slow to adopt new tools, this potential is now being unlocked. At Eclipse Automation, we apply advanced robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and digital technologies to transform how nuclear solutions are designed, built, and maintained.
One exciting development is the ability to create a full digital replica of a reactor and simulate a wide range of operational scenarios, long before any physical assembly begins. This kind of digital twin technology enables teams to optimize designs, improve efficiency, and validate systems with a high degree of accuracy, all while significantly enhancing safety and compliance in a highly regulated industry.
With high stakes on safety and sustainability in the nuclear industry, the emergence of digital twins can foster public sentiment further along the positivity lens, bringing greater confidence to the industry overall.
AI is poised to revolutionize operational areas, such as training, predictive maintenance, and material tracking. By leveraging AI, we can reduce human error, increase uptime, and make smarter decisions based on real-time data.
At Eclipse, we’re also utilizing platforms like NVIDIA Omniverse to enable real-time collaboration in shared digital environments. This allows teams across different locations to visualize complex systems, simulate processes, and integrate AI-driven insights in a highly immersive way. Imagine guiding a technician at a nuclear plant remotely through a maintenance task or providing fully interactive training without ever having to touch the physical equipment. That’s the kind of innovation we are focusing on. Digital transformation in nuclear power is already here, and Eclipse is proud to lead the way.
Tracey: This industry has caught momentum or has now gone mainstream. How do we keep the momentum going?
Greg: Canada’s nuclear industry has evolved significantly over the decades, but the one constant is our position as a global leader in nuclear technology, research, and innovation. While public and political attitudes toward nuclear energy do shift over time, Canada has generally maintained strong support for the industry and its long-term potential.
Today, as we face growing demands for clean energy and sustainable solutions, it is more important than ever for our political leaders to prioritize continued investment in nuclear energy and research. Sustaining Canada’s leadership in this field will require a united effort, one that includes commitment from governments, educational institutions and strong private-sector investment.
Private companies, when working on nuclear projects, also play a critical role in driving innovation to solve some of the most significant challenges of industry. For example, investing in AI and digital technologies that can transform how we manage, monitor, and maintain nuclear systems—especially in remote locations where staffing can be a challenge—can go a long way to enhancing safety and improving operational efficiency.
With all stakeholders working together (across industry, government, and academia), Canada is uniquely positioned to unlock the full potential of nuclear energy and ensure we continue to lead the way in the decades to come.
Tracey: How is Eclipse partnering and working with Indigenous communities?
Greg: Indigenous communities are an integral part of Canada, shaping our history, culture and our country. At Eclipse Automation, we recognize and value the unique contributions, histories, and rights of Indigenous Peoples. We are committed to fostering an inclusive and valuable discussions, especially on crucial topics such as nuclear energy. Getting indigenous stakeholders involved in discussions early on has the potential to benefit the industry overall.
By doing this, indigenous communities can benefit from this growing industry and solve some of their challenges, such as access to sustainable power sources in remote communities. It also gives indigenous communities an opportunity to shape their future by unlocking career opportunities and benefiting from the knowledge and advancements made in the industry.
Tracey: With so much to be optimistic about in the nuclear industry, how would you describe the next 20 years out?
Greg: Nuclear power will be the future of clean energy in Canada and set the tone on a global scale. We are seeing multiple investments being made into nuclear energy, both in Canada and beyond, as governments and the private sector looks to address growing energy demand globally. Canada has shown its leadership in the industry and with current investments it is still forecast to continue to be a leader in the industry.
In the next couple of decades, we predict a few trends will gain traction. The first of which is the deep waste repository in northern Ontario. The need to store spent fuel will only increase as the province invests in nuclear energy refurbishments and new build projects, we will see new areas identified for the safe storage of this material.
However, before the waste is stored, we will see the nuclear waste reprocessed to maximize the value of its life. By reprocessing the waste, i.e. putting it through the reactor a second time, the isotopes will be consumed, and the amount of spent fuel will decrease making it easier to store in the long term.
Additionally, we will see medical isotopes really gain traction. They are currently used today to treat cancer and other diseases, but we will start seeing more innovative applications in the future. For example, isotopes could be attached to proteins which are designed to target and attach to the cancer cells. Once the proteins find these cells, they ‘eat’ them helping to destroy the cancer cells within a patient’s body.
These are just some of the ways the nuclear industry will help improve lives, drive greater efficiencies and become an even cleaner and safer form of energy that we know today.
Wrapping it up
As the nuclear industry continues to evolve, it’s clear that innovation, collaboration, and leadership will be the driving force behind its success. From advancements in Small Modular Reactors and fusion technology to the transformative potential of AI and digital twins, the future of nuclear energy is brighter than ever.
With Canada leading the charge, supported by organizations like Eclipse Automation, the industry is poised to deliver cleaner energy, groundbreaking medical advancements, and sustainable solutions for generations to come.
We extend our heartfelt thanks to Greg Ferguson for sharing his time and expertise, offering invaluable insights into the future of nuclear energy and its transformative impact on the world. Together, we have the opportunity to shape a future where nuclear energy plays a pivotal role in addressing global challenges and unlocking new possibilities.
Explore the possibilities
Want to learn more about the nuclear industry? Contact Eclipse to learn how we support every stage of the nuclear energy lifecycle. With full vertical integration, we deliver end-to-end automation systems that meet the unique challenges of the nuclear sector. Let’s talk!
Related articles and insights
-

Programming the future with Vanessa Loiola: Why robots give us time back
Programming robots means programming a better use of human time.
-
What happens to a $50M assembly line in 5 years? Hidden costs of ignoring lifecycle services
Lifecycle services protect asset value, reduce downtime, and extend equipment lifespan.



